SECURE YOUR BUSINESS WITH EXPERT VAPT STRATEGIES
How Secure Is Your Infrastructure? Book a Free Consultation with Wattlecorp’s Experts to identify vulnerabilities, develop a robust VAPT strategy, and safeguard your business with tailored protection solutions.

We live in an era of technological marvels. Tech enterprises are performing wonders in terms of the solutions and services they provide, making the lives of humans around the globe easier and more efficient.
There’s also the other side of technology that we need to watch out for—the more malicious side. Just as tech experts are striving hard to make our lives more productive, there are unethical tech experts who are doing the exact opposite—that is, coming up with ways to hack and corrupt data to impede the progress of tech enterprises for whatever reason.
An enterprise’s IT security must be strong to repel these attacks by malicious persons, protect its private assets, and safeguard the enterprise from potential financial and reputational damage. And to keep your defences strong, you need to understand your weaknesses and eradicate them.
This is where enterprise or business penetration testing comes in.
Enterprise penetration testing, or pen testing, is the methodological “ethical hacking” of the IT network systems of an enterprise to find the holes in its barricades. These controlled cyberattacks on your system’s defences will give you a detailed understanding of where your underlying security threats are and help you fix them before they are exploited by malicious users.
Table of Contents
Toggle- How Does Penetration Testing Benefit Businesses?
- Types Of Penetration Testing
- How It’s Done: 7 Penetration Testing Stages
- Top Penetration Testing Tools In 2024
- Common Cyber Security Vulnerabilities And Threats Businesses Face
- Ethical and Legal Compliance Considerations
- Choosing A Business Penetration Testing Provider
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How Does Penetration Testing Benefit Businesses?
It is vital to employ regular and thorough pentests for businesses, especially enterprise businesses, and stay on top of security threats, as security breaches by the wrong hackers can lead to financial, legal, and safety repercussions.

Consider the following case: You are a credit rating agency with an extensive database of customer information – private customer information—which, in the wrong hands, can not only harm your end users but can also cause them to lose faith in you as an organization.
Malicious hackers can use your end users’ personal information to subject them to scams or phishing attacks.
Your data breach can inspire your clients to lose trust in your ability to protect their best interests and you might end up losing business.
Your internal security system can be further weakened, leaving your business vulnerable to even further attacks.
Just as a stitch in time saves nine, timely pen tests can help your business be fully prepared for unexpected cyber-attacks, help you abide by cybersecurity regulatory compliance, keep your IT system protected with the latest security tools, and can also help you keep your IT security experts on their toes at all times.
Also Read : Why Your Business Needs A Penetration Test ?
Types Of Penetration Testing
Your IT system’s defences will be unique in comparison to those of other organizations, so the type of penetration testing used will vary from enterprise to enterprise. Let’s take a dive into the various business penetration testing methodologies and understand how each one contributes to a thorough security posture.

Some of the most widely used penetration tests are:
- External Testing will mimic attacking your organization’s external IT networks, such as servers, websites, and web applications that are exposed to the World Wide Web. Sometimes the pen testers are not even allowed within the organization during external testing, so it is done remotely.
- Internal Testing will mimic attacking your organization’s internal IT networks, such as your network servers, internal endpoints, and software applications. Internal tests can give a surprisingly accurate idea of the damage that can be caused to an enterprise if an unsatisfied employee were to go rogue.
- Enterprise Mobile Penetration Testing will involve finding vulnerabilities related to secure encryption, data storage threats, and authentication.
- Web Application Penetration Testing will check the security threats that your web application applications can be subject to, such as remote code execution and SQL injection, among others.
- Cloud Penetration Testing will ensure that your organization’s cloud computing data and infrastructure are secure from external threats that can arise from misconfiguration of cloud resources, incorrect software patching, and unsecured access points.
- Social Engineering testing will check the ability of your employees to safeguard sensitive information and adhere to safe cybersecurity protocols.
- Enterprise Wi-Fi Penetration Testing will help ensure that your wi-fi networks are protected against potential malicious hackers.
- Open-Box Pen Testing in which the pen testers are given a heads up before the testing process and will be equipped with limited knowledge of the enterprise’s security details which will enable them to tackle vulnerabilities faster.
- Closed-Box Pen Testing in which the pen tester goes in with no information about the enterprise he’s about to test the defences of except the name. This test is aptly named a “single-blind” test, as one of the parties involved – in this case, the pen tester—is going in blind.
- Covert Pen Testing, also dubbed “double-blind” testing, takes things up a notch and is one in which both parties are essentially “blind.”. They are organized in such a way that the ethical hacker has limited information about the enterprise, and the company’s personnel, including IT security staff, are also kept in the dark about the test.
Also Read : Manual Penetration Testing Vs Automated Penetration Testing
How It’s Done: 7 Penetration Testing Stages
If you’re wondering how to conduct penetration testing for businesses, look no further. A successful enterprise penetration test will be methodologically executed, and outlined below are the 7 steps for end-to-end cybersecurity testing:
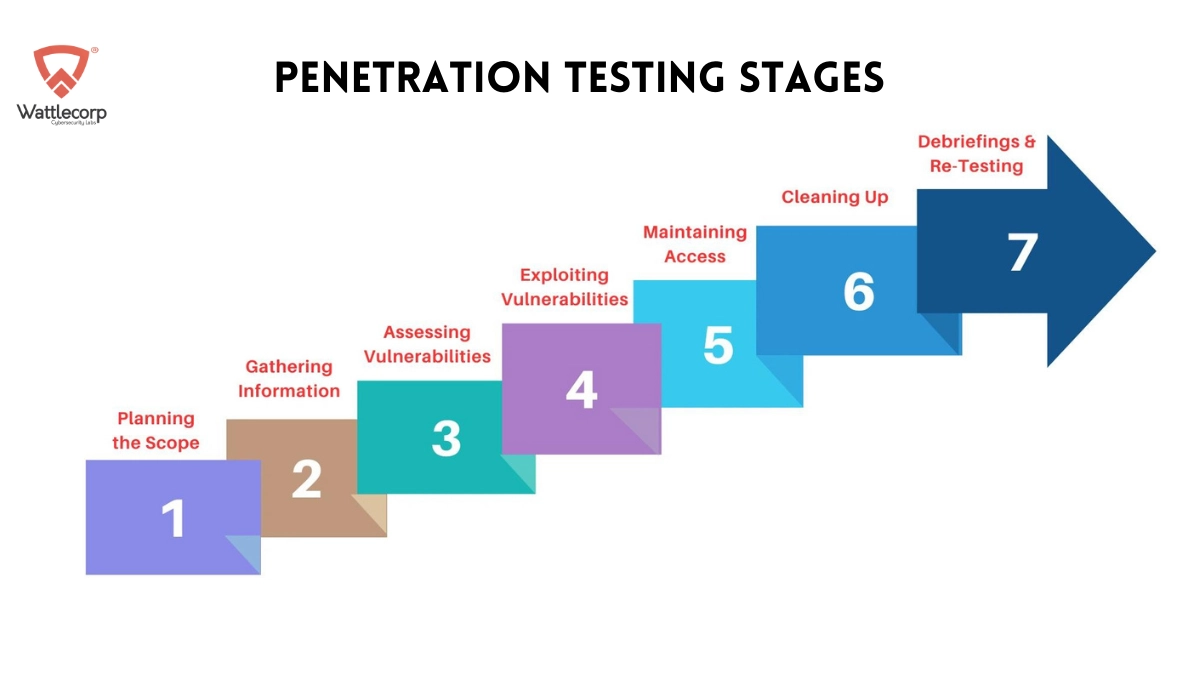
1. Planning the Scope
First things first, you need to understand what sort of penetration testing your business needs and determine the scope of the business penetration testing exercise accordingly. You need to document not only the scope of work, but also the expectations you have of your pen testing service provider, the testing methodologies that are to be employed, and the ethical and legal regulations that must be met while the test is being carried out. This ensures that both you and your testing team are on the same page and your business operation can carry on seamlessly even as your system’s defenses are being tested.
Don’t forget to get an NDA signed by your testers, as there is a high likelihood that they will be able to access sensitive information that is critical to your business processes.
2. Gathering Information
Reconnaissance, that is, gathering relevant information for the testing process, is the second phase of a pen testing endeavor. This is a crucial step that must be done methodically and accurately to facilitate the next phases properly.
In this penetration testing phase, testers use various methods and sources to gain maximum knowledge about the enterprise whose cyber defences they’re testing. This information can come from open-source intelligence, that is, information about the system that is publicly available, or it can be the result of deep research into the organization as well as information gathering from the employees of the enterprise.
However, in most cases where a web application is part of the scope of testing, it is enough to gather the target data from the spiders and crawlers employed on these web applications by search engines to give a detailed insight for experienced pen testers.
3. Assessing Vulnerabilities
In this phase, as the name suggests, the vulnerabilities of the enterprise’s security system are assessed after they are identified using probes into the target system and gather important information. This security vulnerability assessment goes deep to identify the vulnerabilities in the target network. This penetration testing phase is completed once the risks associated with the target system, such as remote code execution vulnerabilities and cross-site scripting possibilities, are quantified and the security audits are documented.
4. Exploiting Vulnerabilities
This is the actual penetration testing phase, where the vulnerabilities that were identified and quantified in the previous phase are exploited actively to see how well the target system holds up in the face of a malicious attack. The attack is carried out with the help of a carefully curated plan of action that has been developed in accordance with the vulnerabilities discovered, which allows testers to go in methodically and try to access the target system through the weaknesses in the systems’ security measures.
While it may not be possible to exploit every vulnerability that was discovered, as the penetration testers’ main focus is on gaining access to the target system, rather than exploiting every vulnerability, every exploitation helps the tester get more in-depth information from the target system.
5. Maintaining Access
Risk assessment in cybersecurity is no joke and requires time to complete. Maintaining access, or lateral movement, is the phase in which testers maintain continued access to the target system once it has been accessed. When a target system is accessed, the IT security administrators might try to reset or reboot the system to cut off the access gained by the testers. In order to avoid the loss of access, testers inject magenta into the system, which takes root in the system and maintains access for as long as the testers want.
6. Cleaning Up
Cleaning up after any work is the worst part for most of us, but an essential one in business penetration testing exercises. This phase is called artifact destruction and includes cleaning up the target system of all software, agents, and temporary files used by the testers.
All the system’s data and configuration, such as credentials and usernames, will be restored to the initial state, thus returning the target system to its normal, pre-tested state.
7. Debriefing & Re-Testing
What’s the point of running an extensive test and documenting the results if they are not properly communicated to the enterprise’s security personnel and management executives? Cybersecurity evaluation results should be concise and easy to understand while detailing the identified and exploited vulnerabilities and how they can be fixed. They must contain both a technical report and an overview that will help decision-makers figure out the next steps.
Once the fixes have been made and the security holes in the target system have been closed, it is always ideal to run a re-test to ensure that the remedying factors were effective after all.
Also Read : Penetration Testing Cost: A Comprehensive Guide for Businesses
Top Penetration Testing Tools In 2024
As unethical hackers find more testing attacks and disrupt IT system networks, some ethical hackers are coming up with more innovative vulnerability analysis tools and technologies to combat cyber security threats.

Penetration testing software and automated scanning tools that are currently on the market, such as open-source operating systems like Kali Linux, Hashcat, and Invicti, are truly remarkable, and each one comes with its own set of advantages. Let us take a quick look at the top 5 most popular penetration testing tools that are available to aid ethical hackers in their quest to enhance enterprise cyber security.
1. Burp Suite: Burp Suite is a one-stop-shop security testing tool that can be used in penetration testing of website applications and can scan and detect vulnerabilities, analyze the traffic between networks, and facilitate deep manual testing techniques.
2. Wireshark: A well-known and widely used network analysis tool that helps you abide by network security protocols and is useful in spotting malicious traffic is Wireshark. Wireshark enables network analysis by capturing and decoding packet data from networks, which helps ethical hackers decipher whether sensitive information is being passed along via a network.
3. John the Ripper: John the Ripper is an open-source password-cracking tool that helps ethical hackers exploit the vulnerabilities of an IT system and is customizable to adapt to various operating systems.
4. Nmap: With advanced features that enable the identification of applications that are vulnerable to threats, Nmap is one of the more popular tools used to scan for open services and ports and is a must-have for most penetration testing processes.
5. Metasploit: Metasploit is another tool that enhances the arsenal of pen testers who are looking to exploit vulnerabilities in an IT environment. It comes with a vast library of exploits for different OS and programs and even has a handy ‘wizard’ that aids ethical hackers in identifying and exploiting known vulnerabilities.
6. Openvas: Using OpenVAS, organizations can detect and eliminate security flaws in their network infrastructures, applications, and servers. The application scans a target environment for vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and weak points.
7. Nessus: It is a tool for conducting penetration tests on your web application and operating system.
8. Frida: Frida is a dynamic analysis tool that lets developers, hackers and reverse engineers embed scripts in software that runs on Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, Android, etc. It is especially useful for analyzing dynamic data, changing the behaviour of applications, and hooking functions.
9. Objection: It allows you to easily perform dynamic analysis by performing runtime exploration, injecting code, and bypassing SSL pinning. Researchers and penetration testers frequently use it for mobile application security testing.
10. Jadx: Jadx is an open-source decompiler for Android APK files that allows reverse engineering and analysis of their bytecode.
11. Reflutter: It allows you to compile, patch, and debug Flutter bytecode, facilitating analysis and manipulation for security researchers and developers.
12. Mobsf: MobSF is an open-source framework for utilizing automated security testing to assess the security of iOS and Android applications.
Also Read : Penetration Testing Frameworks: All You Need To Know
Common Cyber Security Vulnerabilities And Threats Businesses Face
In this penetration testing guide, we’ll take a look at some of the common security vulnerabilities that plague enterprise businesses today and how these underlying security threats can be identified and mitigated with the help of penetration testing service in India.

But, first, let us understand what exactly these vulnerabilities can be and why they must be tackled immediately and effectively.
A vulnerability is a potential risk to the IT security of an enterprise that may or may not be exploited by external malicious agents to undermine the overall cybersecurity of that organization. It is important to address a vulnerability even if it is not purposefully exploited by an unethical hacker because there is still a chance that it can be unintentionally triggered by a non-malicious user.
But whether exploited intentionally or unintentionally, security vulnerabilities will affect your IT environment detrimentally, which is why it is important to detect them from the onset and tackle them before they lead to serious repercussions for your organization, including but not limited to operational disruptions, data loss, or malware issues.
Some of the most common penetration testing vulnerabilities that can cost you dearly if left unattended include the following:
- Zero-Day Vulnerability
When a vulnerability is discovered by malicious agents and exploited before it can be patched (or rectified), it is called a zero-day vulnerability. Such vulnerabilities are very dangerous, as they leave little to no time for your security team to patch them before they are out for malicious use by hackers.
A famous example of a critical zero-day vulnerability is the Log4j vulnerability, a.k.a. Log4 Shell, which was found in November 2021 in the Apache Log4j logging library and allowed hackers full control of all devices that were powered by unpatched versions of the software.
- Improper Data Sanitization
If all the data submitted to a web application is not properly validated before it is processed, it can leave your network system open to attacks like SQL injections ( in which hackers use malicious SQL codes to get access to sensitive information) and buffer overflows (like the infamous Morris Worm that destroyed 10 % of the internet in 1988).
- Unpatched Software Vulnerability
Security patch verification is important. As soon as security vulnerability testing is done and a vulnerability is identified in any software you use, you must waste no time patching it (updating it to ensure that the issue is rectified). Unpatched software leaves the software and security system associated with it vulnerable to cyber attacks that can have far-reaching consequences.
- Misconfigured Settings Vulnerability
If a system’s settings are not configured securely to ensure that the right features are enabled and disabled at all times, it can pose a serious security risk, and this is more prevalent in cloud networks.
- RCE (Remote Code Execution) Vulnerability
If your cyber security does not prevent remote code execution by unauthorized persons, it allows criminal hackers to easily execute malicious code on your system, which can result in a variety of undesirable situations like data breaches and malware that hinder your systems’ operations.
- API Vulnerability
We tend to overlook proper security for APIs as applications are more susceptible to cyberattacks. But this is a common misconception, as improperly secured APIs can also be exploited by malicious users, resulting in tremendous damage to your enterprise.
- Roles and Permissions
Roles and permissions must be assigned sparingly and only to the personnel that require them, as your system becomes more exposed when the number of users with access privileges increases. Wanton’s assignment of roles and privileges can aid hackers in indulging in various cyber crimes such as phishing, credential theft, and stuffing attacks.
Also Read : Penetration Testing Compliances You Should Know
Ethical and Legal Compliance Considerations
It goes without saying that you need to be mindful of information security management. while carrying out penetration tests. This is because you are dealing with confidential and important data, which means you need to abide by certain ethical and legal standards, both as a company and as a pen testing service provider.

There are several excellent data protection and privacy laws and ethical rules that act as guidelines for business penetration testing, which are essentially in place with the same intention but can vary from industry to industry, and this includes ISO 27001, which is a global standard for information management security.
It is easy to ensure that your methods are compliant with industry standards if you take a carefully planned and organized approach to pen testing, which will in turn help you reap all the benefits that come with pen testing while avoiding the pitfalls.
In this penetration testing guide, we shall take a look at some of the ethical and legal compliance aspects of business penetration testing, and how we can navigate related complexities efficiently.
1. Legal Compliance Standards For Business Penetration Testing
The first thing you need to do before proceeding with a penetration test for your business is understand all the legal requirements and regulations you need to comply with to stay on the safe side of the law. Compliance laws for penetration testing vary from industry to industry and also differ with differences in geographical boundaries.
You must be thorough with all the rules that govern your industry and country about business penetration testing while carrying out a controlled pen test for your enterprise.
You should also give due importance to data protection laws that are in place to ensure the privacy and safety of your employees and end users. It is your responsibility to safeguard the personal data that the stakeholders of your business have entrusted in your care while the pen testing process is going on, and this can include safety measures like obtaining proper consent from all concerned parties and making data anonymous to protect the privacy of your stakeholders.
Yet another key point to keep in mind while carrying out an enterprise penetration test is that you do so while fully respecting the intellectual property rights, such as trademarks, patents, and copyrights, of all stakeholders involved directly and indirectly in the testing process.
2. Ethical Guidelines for Business Penetration Testing
Ethical values play an important role in business penetration testing, as it is the ethical responsibility of the pen tester (or ethical hacker) to ensure that the testing methods used do not cause any impairment of the IT networks or infrastructure being tested.
This can be enforced by following the ethical guidelines that were designed to monitor the conduct of the ethical hackers executing PE tests as well as the methods used by them.
Ethical hacking guidelines ensure that pen testers carry out planned pen tests that follow proper authorizations and permissions, respect data privacy, and veer away from methodologies that might potentially harm or disrupt the IT environment of the enterprise whose cyber security is being tested.
Ethical guidelines also make pen testers more cautious while dealing with sensitive information and increase the chances of maintaining user data privacy, as ethical hackers are required to execute careful storage of data and transmit data securely using encryption methods.
Also Read: How To Prepare For Your Annual Penetration Test ?
Choosing A Business Penetration Testing Provider
Your business is unique, so the security needs of your business are also unique. Finding and selecting a penetration testing service provider that can address the unique needs of your business is of paramount importance, as they will follow the best practices in penetration testing for enterprise security.
Before you place the security of your enterprise in the hands of a pen-testing service provider, consider the following questions to determine if they are what is best for your business:
- What are the exact requirements of your enterprise in terms of security protection? This will help you determine the specific kind of pen test required for your business, as the penetration testing process for businesses varies from business to business.
- What are the current strengths and weaknesses of your security team’s efforts? This will help you work out a strategy that will strengthen your security expertise and mitigate the flaws in your defence system.
- How strong is your existing security protection? This will help you understand how often you need to conduct pen tests.

Also, don’t forget to ask and get satisfactory answers from potential pen testing providers to the following questions:
- How skilled is the team of experts who will be hacking your IT defences ethically? Make it a point to evaluate the team you hire and also get references and feedback from their previous clients to understand the pen testing team’s performance capabilities.
- How are they planning to secure your system and your data? Make sure you get liability insurance to protect your interests in case there are any oversights from the testing team.
- What are the methodologies that they are planning to employ? Get an exact understanding of the step-by-step process that your pen testing team is planning to execute, and make it a point to evaluate a sample progress report to make sure you are on the same page.
Now that you’ve understood the importance of penetration testing in business security, you must protect the best interests of your end users and ensure that their confidential data (as well as the data units that are crucial to your business’s operations) are properly secure from internal and external malignant threats.
This is what makes it important for you to carry out properly orchestrated enterprise penetration tests at least annually to test and strengthen the defences put in place by your cyber security team.
While it is important to carry out cybersecurity testing for companies, you cannot do it just for the sake of it or to adhere to compliance with security standards.
It would help if you also entrusted this responsibility to a trusted penetration testing service provider with a team of experts who are well-versed in carrying out different types of business penetration testing using the latest tools and technologies in the market.
Additionally, keep your internal cyber security team and IT professionals up-to-date on the latest ways external threats may penetrate through your firewalls and encourage them to upskill in terms of the latest cyber security innovations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is penetration testing? What is its use in cyber security?
Penetration testing, also known as pen testing, is a method of testing the defences of an IT environment with a controlled attack on the IT system that simulates an external attack by a malicious agent. Pen testing is important in cyber security in IT systems for aiding you in protecting against cyber attacks, finding and fixing the weaknesses and flaws of cyber security practices, and meeting regulatory compliance in cyber security.
2. How does penetration testing work?
In business penetration testing, a cyber security expert will assume the role of an external threat (hacker) and test the defences of an IT system or environment. After finding the underlying security flaws or threats in the system, a pen tester will then compile a detailed report that analyzes the cyber security vulnerabilities and outlines how they can be mitigated.
3. What types of companies need penetration testing?
Any company that relies on digital avenues to bring in revenue, manage its daily operations, and is subject to regulatory security compliance needs network penetration testing. This includes but is not limited to companies that utilize websites and software applications for smooth functioning, such as e-commerce companies, real estate platforms, software-as-a-solution companies, and marketing and media companies.
4. When should you perform penetration testing?
It is ideal to conduct penetration testing regularly for companies that are reliant on software to carry out their routine processes, especially enterprise companies. A penetration test must be carried out at least once a year (if not more, depending on the compliance policies that your company is subjected to) to ensure that your business is properly protected from unwarranted cyber security threats.
5. How do you do website penetration testing?
Website penetration testing can be carried out in three phases. First comes the configuration of your penetration test, which includes understanding the scope of the test and the variables you are testing for, as well as data collection for important aspects such as the architecture of your website, APIs, and website infrastructure. Secondly, ensure that your tests are carried out in compliance with regulatory pen testing policies. Finally, make sure that the gathered results are properly documented and analyzed to understand and mitigate the security risks that your website may be vulnerable to.
6. How do I approach companies for penetration testing?
Before approaching a business penetration testing service provider, make sure you are clear on your requirements and the scope of the pen test you wish to have performed. Then consider various factors, such as the experience of the team who will undertake your pen testing, their reliability and trustworthiness (as you are placing your sensitive corporate data in their hands), and their ability to execute the tests without compromising your day-to-day business operations.
7. How is penetration testing performed for web applications?
Pen testing for web applications consists mainly of four steps: information collation (where you understand the scope of the business penetration testing in detail), research and exploitation stage (where you gather important information required and execute the penetration tests), reporting and recommendations (where you compile all the results of the pen testing and analyze them to give suggestions on how to improve the security defences of your web application), and remediation (where you implement the strategies and processes required to fix the flaws in your cyber security system).
8. How long does a penetration test take?
Penetration tests essentially leave your entire network open to cyberattacks while they are being performed, if not carried out with the utmost precision. Pen tests should therefore be carried out as quickly as possible, and usually do not take more than 1 to 2 weeks, depending on the size and complexity of your enterprise’s IT infrastructure and network systems.
9. What are the steps in a penetration testing engagement?
7 distinctive steps make up a routine business penetration testing exercise, which includes reconnaissance, threat modeling & custom security plans, automatic & custom scripts, developments, identification of zero-day vulnerabilities, exploitation and escalation, cleanup and reporting, retesting, and certification.








