Table of Contents
Toggle- What is NCA ECC and Why Saudi Businesses should consider implementing it?
- What are Essential Cybersecurity Controls (ECC) and why do they matter for Saudi businesses?
- How to Implement Essential Cybersecurity Controls (ECC – 2:2024) for Saudi organizations?
- How does NCA ECC relate to other Saudi cybersecurity frameworks and compliance standards?
- What are the benefits of implementing ECC 2 for Saudi businesses?
- Implementing the ECC-2:2024 Framework for Saudi Arabian Businesses
- Common implementation challenges and solutions that ECC – 2:2024 Pose for Saudi businesses
- Industry-specific considerations for implementing the new ECC update
- Measuring Success and Compliance with ECC-2:2024 Implementation for Saudi Businesses?
- NCA (ECC) FAQs
What is NCA ECC and Why Saudi Businesses should consider implementing it?
If you’re a business operating in Saudi Arabia, you know how important it is to abide by the stringent laws and regulations prevailing there. You must also be aware of the penalties of not complying with them. If these aren’t enough, there are the challenges of implementing security measures, which should also align with compliance requirements in this Middle-East land.
Whether you’re a government entity or operating in the private sector, ensuring strict cybersecurity standards is crucial.
With Saudi Arabia having initiated its Vision 2030 strategy, for attaining economic, social, and technological progress, this does necessitate linking those efforts with the nation’s cybersecurity regulations, specifically NCA to derive value.
The National Cybersecurity Authority (NCA) was established in October 2017 as a move to safeguard its critical infrastructure from the harmful clutches and impact of cybercrime.
With the NCA having introduced Essential Cybersecurity Controls (ECC), these are designed to strictly safeguard the critical national infrastructures in Saudi Arabia.
As this blog unfolds, we will look into:
- Why Essential Cybersecurity Controls matter for Saudi organizations?
- What’s the latest (2025) ECC update?
- Who should implement ECC 2 (ECC – 2:2024)?
- Essential steps to implementing ECC 2 to stay ahead of threats and attacks.
What are Essential Cybersecurity Controls (ECC) and why do they matter for Saudi businesses?
Understanding Essential Cybersecurity Controls (ECC)
The Essential Cybersecurity Controls launched by Saudi’s NCA is o set of baseline cybersecurity requirements for businesses to meet in the Kingdom.
ECC was born from an extensive study of the various national and international cybersecurity frameworks conducted by the NCA. This involved:
- A detailed analysis of existing law and regulatory requirements and related decisions.
- Evaluating previous incidents and attacks on the government organizations and businesses operating under critical sectors.

The Essential Cybersecurity Controls functions as an assessment and compliance tool for Saudi businesses. Implementing these controls or standards can help organizations identify, access, and manage cybersecurity risks and threats and set the path for evaluating compliance against the relevant framework.
The ECC standards comprise:
- 5 major domains of cybersecurity
- 29 sub-domains
- 114 controls
A Look into the Latest ECC Update
With the ECC – 1:2018 updated to ECC – 2:2024 as of October 2024, this will serve to enhance cybersecurity efforts by streamlining the security and compliance process. This is through reducing the controls from 114 down to 108, all with an intent to improve the security posture for the Kingdom.
- Incorporate newer enhancements for addressing emerging cyber threats
- Improve overall cyber resilience for the Kingdom
As per the NCA’s updated information, ECC – 2:2024 is also bound to minimize risks secondary to quantum vulnerabilities and those challenging supply chain functions.
It also encompasses regulatory and compliance considerations that go beyond understanding ECC as a minimum cybersecurity standard and include:
- Undertaking a comprehensive assessment of gaps by utilizing NCA toolkit
- Implementing controls across five domains (governance, defense, resilience, ICS, and Third Party or Cloud).
- Establishing ongoing monitoring with regular updates, and continuous verification for compliance for safeguarding Critical National Infrastructure and sensitive data.
Besides these, you’ve more key areas to focus on, including ECC framework alignment, data and technological assets protection, and building a dynamic compliance landscape.
Above all, the ECC 2 will serve as a lesson from previous incidents and attacks on critical government entities. It holds promises for ensuring continuous commitment to combat high-profile, AI-powered cyberattacks.
Who should comply with the NCA Essential Cybersecurity Controls?
The NCA ECC essentially applies to organizations that operate within the government and private sectors. The framework is specifically meant for those who own, operate, and manage Critical National Infrastructures (CNIs).
- Government Entities: Include authorities, ministries, establishments, and businesses functioning in similar public sectors.
- Private Sector Organizations: Energy, finance, healthcare, and telecommunications.
The NCA ECC is not confined to the aforementioned public and private sector organizations in Saudi Arabia. Every other entity, be it an SME or even a startup should consider complying with this cybersecurity framework. Adhering to this to secure their vital assets is one of the best practices to ward off cyber threats before they strike.
How to Implement Essential Cybersecurity Controls (ECC – 2:2024) for Saudi organizations?
Implementing Essential Cybersecurity Controls warrants a 5-step implementation framework, one that maximizes your potential for achieving strategic outcomes and organizational scalability..
Know then that this process involves a 5-step implementation framework. Let’s see what they include:
Stage 1: Foundation and Assessment
- Performing a comprehensive security audit with risk assessment
- Prepare a detailed list of assets, systems, and data processes
- Creation of a governance structure and baseline security policies
- Implementing user authentication and basic access controls
Stage 2: Core Protective Controls
- Endpoint protection and antivirus solutions deployment
- Network segmentation and firewalls implementation
- Creation of a secure backup and recovery processes
- Establishing basic logging and monitoring systems

Stage 3: Advanced Detection and Response
- Deploying Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems
- Implementing intrusion detection and prevention systems while establishing a prompt incident response plan with development of cybersecurity teams to handle the process.
- Performing vulnerability assessment with patch management.
Stage 4: Secure Measure Enhancements
- Multi-factor authentication implementation
- Developing and deploying solutions to prevent data loss
- Training on security awareness
- Implementing and improving threat-hunting capabilities
Stage 5: Continuous Improvement and Optimization
- Undertaking regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing
- Implement continuous monitoring and threat intelligence mechanisms
- Offer regular policy updates, combining them with compliance audits
How does NCA ECC relate to other Saudi cybersecurity frameworks and compliance standards?
Acting as a foundational framework for cybersecurity, NCA ECC’s can well blend with other relevant and specialized cybersecurity frameworks in Saudi Arabia.
Also Read : Preparing for NCA ECC Audits: Implementation Guide for Your Business
NCA ECC, by incorporating specific aspects from national (SAMA, SCyWF) and international (NIST and GDPR) standards, can effectively help secure Saudi businesses. Ongoing security is what leads to ensuring compliance with these regulatory frameworks.
Now, let’s look into how NCA ECC adapts to similar cybersecurity regulations in the Kingdom.
Cultural and Regulatory Adaptations
Foundation and Regulatory Compliance Assessment Pertaining to NCA (Months 1-2) – Stage 1
- Performing security audits that align with NCA’s ECC
- Charting current infrastructure against relevant cybersecurity frameworks
- Establishing a governance structure that adheres to the Vision 2030 digital transformation goals.
Implementation of Shariah-Compliant Core Controls (Months 3-4) – Stage 2
- Developing and deploying Halal-certified security solutions.
- Implementing data-residency controls to ensure sensitive data stays within Saudi borders
- Establishing backup procedures that adhere to local data protection laws
- Setting up monitoring systems that place cultural and privacy concerns in prime considerations
SAMA and CITC Regulatory Alignment (Months 5-6) – Stage 3
- Implementing controls for the financial to comply with SAMA (Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority) standards
- Complying with the telecommunications and information technology regulations as per the Communication and Information Technology Commission (CITC) requirements
- Establishing NCA-aligned incident-reporting mechanisms (identifying, documenting, and reporting cybersecurity incidents).
- Installing threat detection mechanisms to meet Saudi’s CERT requirements.
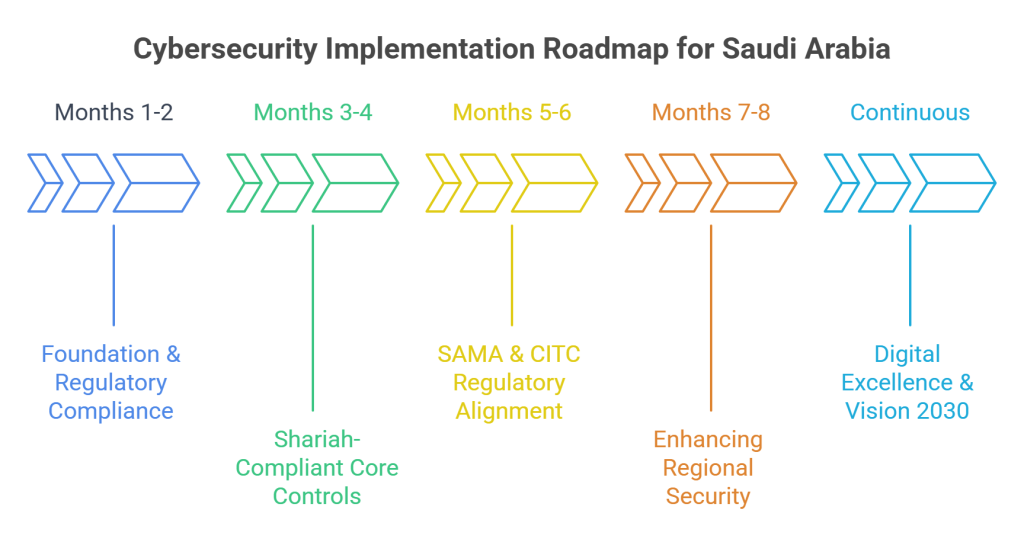
Enhancing Regional Security (Months 7-8) – Stage 4
- Offering comprehensive training to Saudi employees for implementing bilingual language (Arabic and English-based security measures.
- Deploying region-specific threat intelligence measures (gathering, analyzing, and acting on intelligence feeds received).
- Partnering with local cybersecurity service providers
- Implementing robust proactive security measures, such as Data Loss Prevention (DLP) to get past evolving Saudi-specific data protection regulations
Achieving Digital Excellence Through Vision 2030 (Continuous) – Stage 5
- Making sure that the implementation aligns with NEOM and other smart city cybersecurity initiatives
- Integration with Saudi’s national digital infrastructure
- Engaging in threat-sharing initiatives in the MENA region.
- Contributing effectively to Saudi Arabia’s goal of becoming a regional cybersecurity hub.
What are the benefits of implementing ECC 2 for Saudi businesses?
Unlike its previous version, i.e., ECC – 1:2018, ECC – 2:2024 will strive to strengthen cybersecurity in the Kingdom through efforts that include:
- Offering key updates and additions from previous versions
- Alerts on emerging threats associated with AI and cloud service usages, as well as supply chain threats with steps to mitigate and resolve them
- Enhanced focus areas (remote work, IoT security, etc.)
- Helps streamline the implementation process by reducing controls (from 114 to 108).
In addition to these, the new ECC – 2:2024 framework adoption will deliver:
- Strategic and operational advantages
- Providing clearer guidelines and advanced controls for advanced protection of digital assets and critical infrastructure
- Direct Vision 2030 goals.
- Enhance regulatory compliance for financial enterprises and businesses operating within the critical private sector.
- Improved confidence and trust among stakeholders, international partners, and regulators
- Comprehensive threat protection from emerging threats by focusing on asset management, network security testing, cryptography, and Identity and Access Management (IAM).
- Alignment with international standards, such as NIST Cybersecurity Framework, ISO 27001, etc., to foster global connections and increase business expansion opportunities.
- Operational maturity by encouraging businesses in Saudi to derive improved security maturity besides demonstrating efficient control implementation.
In summary, these beneficial features do strongly speak for achieving sustainable competitive advantage for businesses.
However, these efforts can only bear fruit if the newly updated ECC controls are implemented sensibly.
Implementing the ECC-2:2024 Framework for Saudi Arabian Businesses
No matter, whichever cybersecurity framework you implement as a business in Saudi Arabia, the key to its successful execution is always a standard-cum-structured approach adopted therein, especially concerning ECC – 2:2024 implementation.
Risk-based Implementation
- Involves identifying and assessing potential vulnerabilities and associated risks, prioritizing and mitigating them based on their severity and impact.
- Undertaking targeted implementation of security measures and effectively allocating resources with budget considerations.
Understanding the Framework Architecture
Offers a more streamlined architecture by reducing high-level domains down to 4, subdomains to 28, controls to 108) for an effective implementation.

Strategic Implementation Methodology
- ECC 2 offers a more structured approach to manage cyber risks to improve resilience and build trust among stakeholders across all levels.
- A phased implementation process helps ascertain a systematic and efficient incorporation of each domain.
Four-Domain Strategic Focus:
Helps naturally integrate the 4 key cybersecurity domains (governance, defense, resilience, and third-party or cloud computing services) of the ECC framework.
Common implementation challenges and solutions that ECC – 2:2024 Pose for Saudi businesses
While ECC – 2:2024 provides various benefits, there also exist specific challenges when implementing the essential controls therein. However, these do not go without appropriate solutions tackling them. Let’s look at these:
Challenge #1: Evolving Regulatory Requirements: Adapting to evolving regulatory standards pose major challenges for Saudi businesses. Maintaining compliance can prove even more exhausting.
Solution: Establish a dedicated team with clear ownership for appropriately mapping and implementing the essential cybersecurity controls. This should also consider developing automated policy management systems and standardized template creation for quick updations as regulations evolve.
Challenge #2: Tier-based Complexities in Compliance: The adoption of the tier-based compliance model is a major change that imposes significant challenges to ensuring compliance. With organizations classified as Advanced, Essential, and Minimal under this model, risks can only be mitigated based on their level of criticality and exposure. Determining what requirements they should comply with can be pretty confusing in this scenario,
Solution: Conducting a thorough risk assessment for an organization can help determine appropriate tier classification. Partnering with experienced cybersecurity professionals in the NCA guidelines can also help ascertain which firm belongs to which tier for developing accurate solutions.
Challenge #3: New Saudi-based Requirements: Include key challenges related to the amendments to the ECC scope, also authorization transfer per data localization, and new Saudization requirements. Businesses in these cases should ensure proper Saudi national representation in regards to seeking cybersecurity service.
Solution: Planning and developing a comprehensive workforce can help solve this crisis by combining Saudi National Talent Development and Knowledge Transfer Programs. Consider implementing mentorship structures, enrolling in advanced certification programs, and investing in local cybersecurity education to aid in this.
Industry-specific considerations for implementing the new ECC update
Saudi’s NCA ECC – 2:2024 sets specific cybersecurity compliance mandates for industries functioning across public and private sectors.
As you know, Energy & Utilities, Banking & Fintech, and Healthcare come within the critical infrastructure sectors.
- Energy & Utilities: Protecting industrial control systems and maintaining critical infrastructure resilience with enhanced focus on operational technology.
- Healthcare: Safeguarding patient data privacy, ensuring healthcare data integrity, securing medical devices, and considerations for continuity of care.
- Government Entities: Security enhancements for sensitive government data, securing inter-agency communications, and protecting critical citizen information.
- Banking & Fintechs: Placing emphasis on protecting critical financial data, ensuring payment system security, preventing fraudulent practices, and aligning operations with regulatory compliance requirements.
With ECC being updated to ECC – 2:2024, organizations across industries can reasonably expect a streamlined process, thanks to this new update reducing controls from 114 to 108.
Measuring Success and Compliance with ECC-2:2024 Implementation for Saudi Businesses?
For determining the success and compliance potential of implementing ECC – 2:2024 by Saudi business entities, this follows a multi-layered approach. While on one hand, this framework helps verify compliance with relevant regulations, on the other, it does ascertain appropriate strategic performance through the below-mentioned parameters:
- Key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics: Measures your overall compliance percentage against all controls (110, reduced to 108).
- Assessment and audit considerations: Undertaking proactive measures that identifies underlying vulnerabilities, assessing, prioritizing, and mitigating them based on their risks, severity, and impact.
- Reporting and documentation requirements: Preparing a detailed document presenting a list of identified security flaws, also describing them with appropriate and actionable recommendations offered.
- Continuous monitoring approaches: Performing real-time monitoring for threat detection, promptly improving incident response rates, and strengthen security posture.
- Operational Excellence: Improving incident response rates by adopting strategies, such as Mean Time To Detect (MTTD) and Mean Time To Respond (MTTR). It also includes your ability to provide security awareness training to employees and conducting secure assessment for third-parties.

With businesses flourishing in the Kingdom, it’s natural for cyber threats to gain entry into unprotected windows and websites to steal sensitive data and cause security havoc.
For a nation, who thrives on critical assets to acquire full-fledged development, implementing security controls of a higher order goes far from being an obligation.
Implementing the new NCA ECC – 2:2024 not only ensures adherence to existing cybersecurity standards in Saudi Arabia, but is also set to drive its Vision 2030 goals. From closing security gaps to improving incident response rates, the new ECC implementation strategy can help foster a cyber risk-resilient economy for Saudi Arabian businesses.
Though compliance requirements vary across industries, they can significantly improve cyber resilience, improve cybersecurity posture, and reduce penalties to a remarkable extent.
Also Read : The Intersection of NCA ECC and Data Privacy: Ensuring Comprehensive Protection
Acquiring such an outcome, however, mandates hiring professionals with expert knowledge, who can guide and handle the implementation procedure flawlessly.
Cybersecurity professionals should be aware of the existing threats and demonstrate efficiency to navigate across various compliance requirements in Saudi Arabia.
If you’re serious about achieving both security and compliance through effective and error-free NCA ECC implementation, then Wattlecorp is your destination.
From receiving multiple accolades for offering matchless security services to clients worldwide to developing an ardent understanding of the strict cybersecurity rules and regulations existing in a land like Saudi Arabia, Wattlecorp is one you can confide in for all your security and compliance needs.
Where sustainability and competitive advantage merge with continued efforts to stay protected, being updated with Saudi’s NCA ECC standards will be your stepping stone to achieve such a milestone.
Visit our NCA Compliance Services in Saudi Arabia service page to gain a better understanding on meeting NCA ECC standards for your business in the Kingdom.
Ready to bolster your cybersecurity posture with Saudi’s new NCA ECC update? Partner with Wattlecorp for an expert-led ECC – 2:2024 implementation guidance.
Achieve ECC-2:2024 compliance. Contact Wattlecorp Today!
NCA (ECC) FAQs
1.What is the NCA cybersecurity framework – 10-100?
The NCA cybersecurity framework (NCA CSF) 10-100 represents a domain or control number existing within the larger Critical Systems Cybersecurity Controls (CSCC) framework. Both Essential Cybersecurity Controls (ECC) and CSCC coming under NCA are meant to help strengthen cyber resilience and security posture for Saudi companies.
2.Are there any training and certification opportunities for implementing NCA ECC?
Yes, there are. Organizations in the Kingdom should develop and approve cybersecurity awareness programs through multiple channels. These need to focus on both current and evolving cyber threats and risks to build a positive cybersecurity culture.
The Saudi NCA provides official regulatory documents with implementation guidelines, which you can download through their website.
Aligned with both national and international cybersecurity standards, the ECC framework helps add relevance to the existing cybersecurity certifications.
In addition to these, you can obtain specialized NCA ECC compliance training and certification programs that third-party consulting firms and cybersecurity companies provide.
3.What are the penalties for non-compliance with NCA cybersecurity regulations in 2025?
Industries and companies not complying with the updated NCA cybersecurity regulations in Saudi Arabia are bound to suffer penalties in terms of:
● Hefty fines of up to SAR 25,000,000.
● Administrative warnings including temporary or permanent license suspension.
● Reputational impact arising from lost trust and confidence from clients, customers, and investors.
Note that these penalties across different cybersecurity regulations in the Kingdom, where the amounts are determined according to the nature and severity of the violation.
4.Does NCA ECC compliance apply to small businesses and startups?
Yes, even though NCA ECC compliance critically applies to governments and private organizations that own, operate, and manage Critical National Infrastructures, smaller businesses and startups are also encouraged to implement those controls.