Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Data Portability
Data portability is a process where individuals collect the personal data they have already shared with a service provider and reuse it for their purposes across other services for better options. This means you can port data from one company to another when needed.
You can have access to the same data by transferring it to another controller without any hindrance. The portability works only when the individual provides consent and the data is processed. With the permit right from the user, the processing is carried out by automated means.
The intention behind this right is to port data to multiple devices as per the user’s preference. Data portability is designed to transfer user data that has locked users on a long-term basis into a single platform or provider.
Here is a simplified version with an example: Imagine you are a subscriber to a music streaming service, and you want to try a different service. With data portability, you can transfer your playlists and preferences to the newly chosen service provider. And you don’t have to enter every data you prefer manually.
Why Data Portability Matters in Indian Business Setups
Data portability empowers users in several ways. It removes friction in moving between services. You can easily choose platforms based on quality and not on the weight of personal history that has been held hostage in the previously used platform.
From a market perspective, this porting right encourages competition and innovation. When users can freely take their data elsewhere, it is a sign that better offers can lure the customers away. So, in order to sustain customers, companies must focus on offering better services rather than locking them.
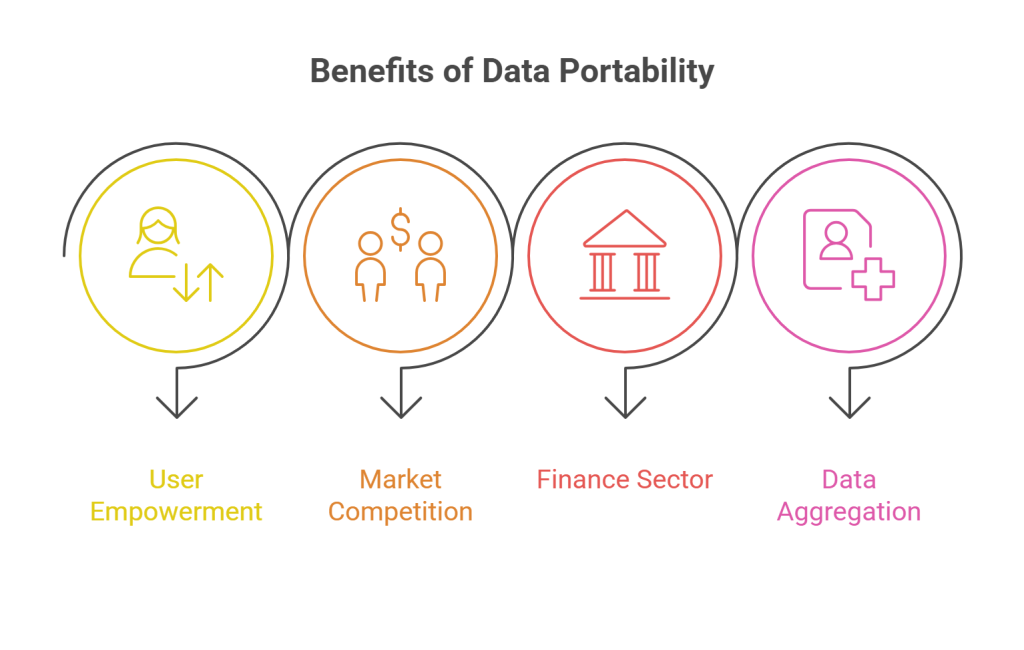
In the finance sector, for example, open banking initiatives designed with the capability of data portability are already enabling customers to switch banks more easily. They can access personalized financial services, meanwhile they also have the option to integrate their accounts into third-party budgeting tools.
In banking, it is beneficial on a personal level, but in other sectors, individuals can aggregate data from multiple sources for deeper insights. For instance, you might be using a nutrition app to track your fitness data, and if you could integrate your medical records too, it could provide a complete report of your health.
What Is Interoperability?
While the legal proof that leads to portability is enabled, its effectiveness majorly depends on interoperability. This means the system or service provider you choose must have the infrastructure and compliance to exchange and interpret information smoothly. Without this, portability is not practically possible, as it is interwoven.
Here is a reference: Imagine you have posts on a social media platform, and you could extract the data only in a proprietary format that cannot be read by the competitor system (your newly chosen service provider). This means there is no interoperative capability where you technically have your data, but you cannot use it.
Also Read : What SaaS Providers Need to Know About India’s Digital Personal Data Protection Act 2023
Interoperability ensures that when data is transferred, it can be rightfully transferred to the receiving service without losing quality, structure, or context. True interoperability requires standardizing file formats, data fields, and transfer protocols so that data remains meaningful across systems and is accessible on different platforms.
India is one step ahead in practically applying interoperability in UPI. The record states that 24.03 lakh crore INR is processed in payments, especially during the period of June 2025, which is a 32% increase compared to the previous year.
Challenges in Data Portability and Interoperability
Technical Complexity of Data Portability
Transferring personal data from one service provider to another may seem easy to picture, but it requires a strong technical foundation. Data needs to be extracted, formatted, and delivered in a way that is both usable and secure. Many organizations struggle with data format inconsistencies, as each business follows a varied structured format in storing data.
In other cases, many are working with legacy systems, and these older IT infrastructures are often incompatible with modern export tools. Also, when dealing with large datasets, multimedia files, and mixed data types, they need more processing power and time to transfer safely.
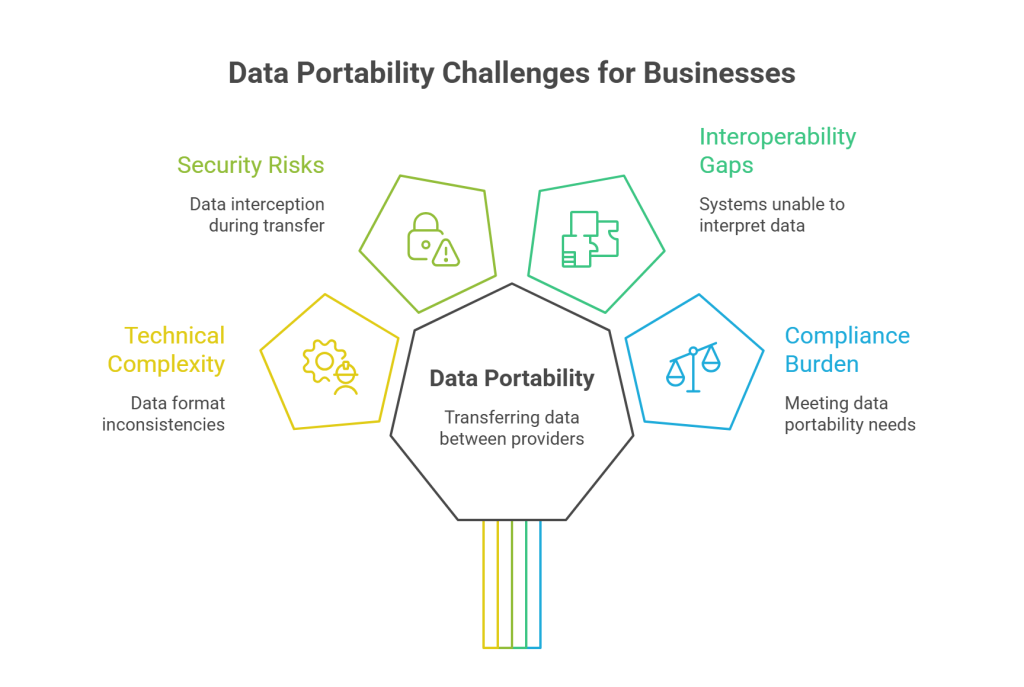
When there are no robust internal systems, even a lawful request for portability can be complex to process.
Security Risks During Transfer
Porting data to a new service provider comes with security risks. The risks can be like data interception by malicious actors during transfer. If there is a lack of encryption or weak authentication methods followed, then your data is vulnerable to threats.
Under GDPR, organizations must ensure secure transfer channels. However, the added risk is that adhering to these standards can require significant investment in encryption protocols and verification procedures.
Interoperability Gaps Between Systems
Interoperability means different systems and organizations can work well together, and this works smoothly when data can be transferred easily between them. Without it, even if data is exported in the right format, the receiving system might not be able to interpret or use it effectively.
The gaps can be due to several reasons: it include a lack of common standards for file formats and metadata. Some businesses lock users into a single ecosystem, and it is hard to port data. Each business stores data in unique structured formats, and there might be semantic mismatches, where the meaning of data elements differs between platforms.
Also Read : The Role of Data Protection Officers in SaaS Companies: A Mandate Under the DPDPA
Compliance Burden for Businesses
Meeting the EU’s GDPR or India’s DPDPA for data portability needs is a compliance challenge rather than considering it as a technical task. Businesses are obliged to create clear policies and processes for handling requests. In addition, they are supposed to maintain records of portability requests for audit purposes.
Mandating these requirements for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) is challenging, especially when they lack dedicated compliance teams.
Why Don’t Every Country Mandate Data Portability
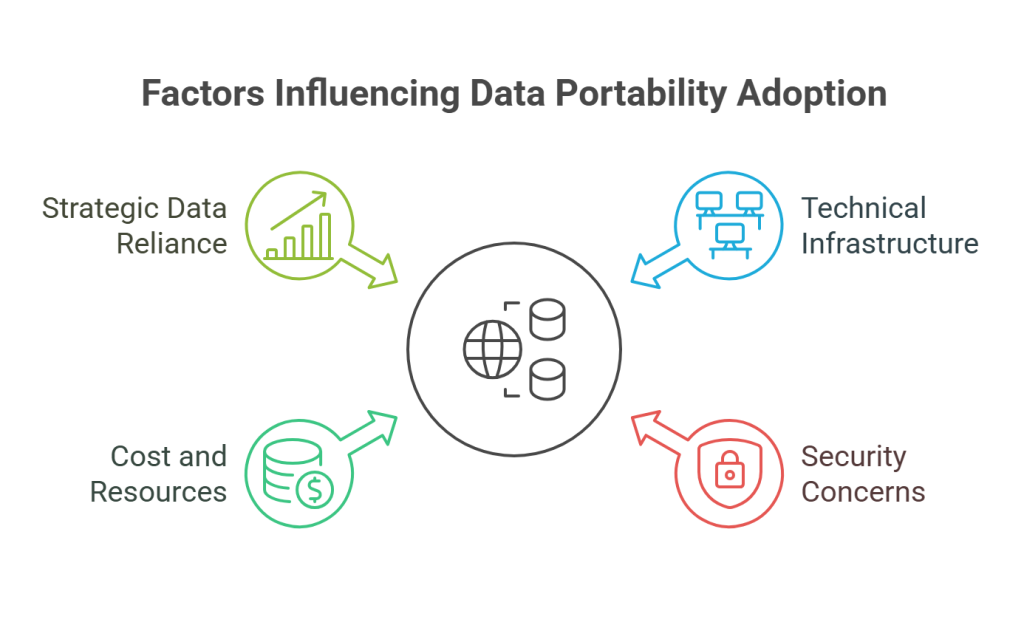
Outside the EU, the adoption of data portability rights is not strictly followed. Some countries have decided not to mandate it for multiple reasons, like the lack of technical infrastructure needed to support secure and effective portability.
There are other countries concerned about the increased risk of data breaches. Another reason to fear is the potential for malicious exploitation of transfer systems. For smaller companies and startups, implementing portability mechanisms can come with heavy costs and require many resources.
Some organizations that rely on customer data as a strategic asset may be reluctant to support easy switching. They mainly fear loss of market share and loss of proprietary advantages once customers can easily take their data elsewhere
Data portability and interoperability operate without any crash when the privacy rules are strictly adopted. When there is an absence of a strong regulatory foundation, sharing or moving data between systems can be risky. It will lead to security risks and you might ever face loss of customers.
The data portability in India is managed under the Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDPA). When you are setting up data portability access, it is important to know about the DPDPA law of India and incorporate it into your practices. And you need a skilled professional to align your business with the privacy regulations of the country.
At Wattlecorp, we have well-trained data privacy experts who help businesses meet DPDPA requirements. We ensure strict adoption of data protection laws for smooth and secure data transfers.
DPDPA Compliance FAQs
1.What does the Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDPA) mean for businesses in India?
The DPDPA is a personal data protection act. It lists out the rules for how businesses in India must collect, store, use, and share personal data. Under this, businesses must ensure transparency, security, and user rights protection.
2.Is DPDPA compliance mandatory for all companies operating in India?
Yes. Any company in India or outside nations dealing with the personal data of people in India must follow DPDPA guidelines. Refraining from this law might pose you with penalties.