Table of Contents
ToggleHow to Successfully Manage SAMA Compliance and Avoid Common Pitfalls
To fortify the financial sector against cyberattacks, Saudi Arabia has realised the SAMA cybersecurity framework. Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority (SAMA) and the National Cybersecurity Authority (NCA) are both at the forefront of pushing forward different regulations to safeguard the financial sector during the rapid digital transformation.
Whether you’re a bank, fintech, insurer, or payment gateway, this blog is your 2025 guide to SAMA readiness. Here we have outlined seven common pitfalls businesses fall into when it comes to SAMA compliance and how to avoid them. Learn the expert strategies of Wattlecorp’s SAMA compliance services that will help you get aligned with Saudi regulations.
What is SAMA Compliance?
The Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority (SAMA) is the central bank that plays a critical role in regulating the financial sector of KSA. SAMA is primarily responsible for supervising commercial banks, issuing national currency, overseeing foreign exchange reserves, and introducing compliance measures for sound practices in the financial sector.
The Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority (SAMA) implements a strict Cybersecurity Framework to safeguard the financial infrastructure and consumer data. The SAMA cybersecurity framework is a set of guidelines that all financial entities in KSA are instructed to follow.
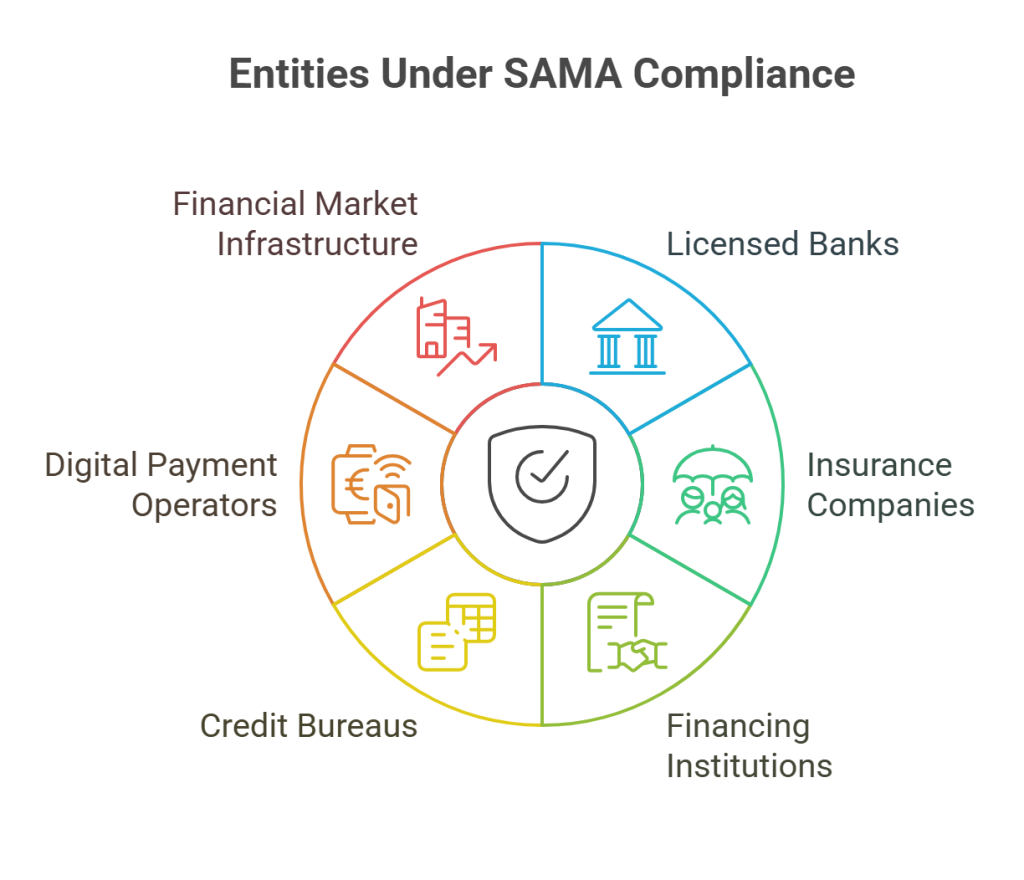
SAMA CSF applies to the following Member Organizations that are licensed by SAMA, including:
- All licensed banks operating in the KSA
- Insurance and reinsurance companies based in Saudi Arabia
- Financing and lending institutions across KSA
- Credit bureaus and digital payment operators
- Operators of Financial Market Infrastructure within the Kingdom
SAMA Cyber Security Framework Control Domain Requirements
The SAMA Cybersecurity Framework is organized into four control dimensions, which have different areas of concern. Combined, these domains create an elaborate security posture covering protection, resilience, and accountability in the financial entities of Saudi Arabia.
1. Cyber Security Leadership and Governance
The top-down perspective the domain for which we must maintain the maturity of cybersecurity. It requires the management to be actively engaged in the planning, execution, and evaluation of cybersecurity programs.
Key Requirements:
- Creating a Cybersecurity Governance Committee.
- Appointment of a CISO or similar security-related role.
- An enunciated Cybersecurity Strategy aligned with the enterprise.
- Management and board involvement for cybersecurity matters.
2. Cyber Security Risk Management and Compliance
This domain is concentrated on those technologies and processes that the organisation needs to protect itself against cyber threats.

Key Requirements:
- Implementation of endpoint protection, firewalls, intrusion detection/ protection systems (IDS/IPS).
- Use of secure configurations and patch management for systems and devices.
- Central logging and real-time security monitoring with the help of SIEM Solutions.
- SDLC documentation for internal and third-party applications.
- Data is encrypted at rest, and backup and disaster recovery practices are in place.
3. Cyber Security Operations and Technology
This sub-domain refers to the cyber threats that external suppliers and service providers present.
Key Requirements:
- Deployment of endpoint security, firewalls, IDS/IPS.
- Secure hardening and patching of systems and networks.
- SIEM Centralised Logging and Continuous Security Monitoring.
- Strong SDLC in place for internal and third-party applications.
- Encrypted data in transit, secure backups, and disaster recovery plans.
Also Read : Achieving SAMA CSF Compliance: Step-by-Step Implementation for Fintechs
4. Third-Party Cyber Security
This area focuses on the cyber threats posed by external vendors and service providers.
Key Requirements:
- Before onboarding, conduct adequate risk assessment and due diligence on all third parties.
- Setting up TPRM frameworks and SLAs with a cybersecurity clause.
- Ongoing oversight of vendor’s security posture.
- You shall audit and request evidence of controls from vendors with access to sensitive data and systems.
Common Pitfalls of SAMA Compliance & Tips to Avoid Them
1. Misinterpreting the Scope of SAMA Regulations
The Pitfall : Some organisations treat compliance as the responsibility of only IT or cybersecurity teams.
The Solution : SAMA compliance necessitates collaboration across departments, including operations, HR, and executive leadership. At Wattlecorp, we help businesses establish cross-functional compliance strategies that embed accountability at every level.
2. Incomplete Risk Assessment and Asset Inventory
The Pitfall : Poorly maintained asset inventories lead to gaps in security controls.
The Solution : Use automated tools for asset discovery and risk classification. Wattlecorp ensures your inventories are comprehensive, current, and linked to control baselines.
3. Neglecting Third-Party Vendor Risks
The Pitfall : Many firms overlook the compliance posture of external vendors.
The Solution : Develop a Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) strategy. Wattlecorp assesses vendor security policies and integrates them into your overall SAMA compliance framework.
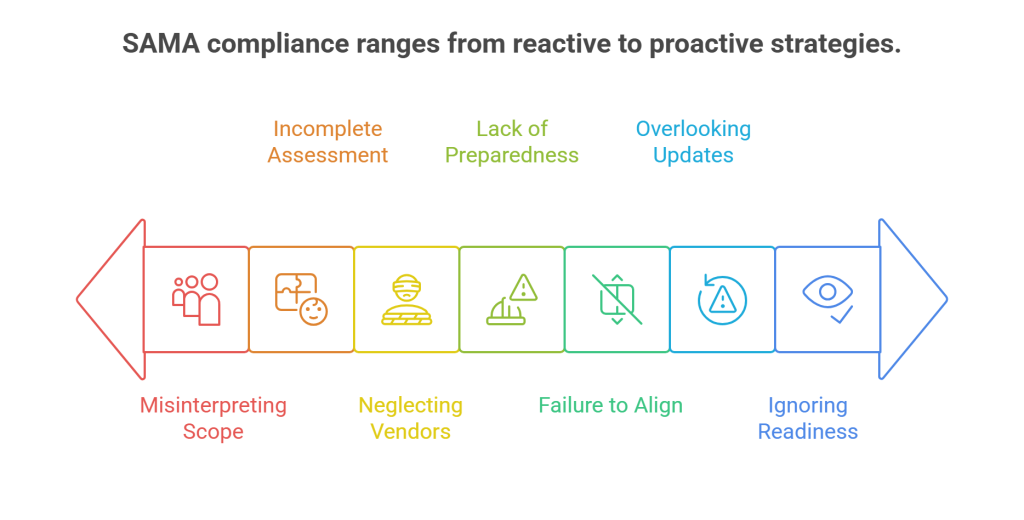
4. Lack of Incident Response Preparedness
The Pitfall : Incident response plans are often outdated or untested.
The Solution : Create, document, and regularly test an Incident Response Plan (IRP). Wattlecorp conducts cyberattack simulations to evaluate your detection and recovery capabilities.
5. Failure to Align with SAMA’s Cybersecurity Governance Domain
The Pitfall : Without formal governance, compliance efforts remain reactive and inconsistent.
The Solution : Appoint a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) or similar executive role and establish a Cybersecurity Governance Committee. Wattlecorp can assist you with regarding policy drafting and governance reporting.
6. Overlooking Continuous Compliance and Audit Readiness
The Pitfall : One-off compliance checklists do not ensure long-term alignment with evolving SAMA standards.
The Solution : Implement continuous monitoring and audit processes. Our SAMA compliance services include dashboards that track your compliance in real-time and prepare for regulatory reviews.
Also Read : SAMA Compliance as a Competitive Advantage: Enhancing Trust and Security in the Financial Sector
7. Ignoring Localised SAMA Regulatory Updates in Saudi Arabia
The Pitfall : Businesses often miss updates published by SAMA or the Saudi Data & AI Authority (SDAIA).
The Solution : Subscribe to regulatory feeds and partner with local compliance experts like Wattlecorp.
Proactive Steps to Ensure Saudi Arabia’s SAMA Compliance in 2025
Staying compliant with SAMA regulations in 2025 means moving beyond one-time audits to building a culture of continuous security. The following are the major steps to stay ahead:
- Conduct a Gap Analysis
Identify areas of non-compliance and prioritise fixes with expert-led assessments. - Build a Cross-Functional Team
Compliance should involve IT, HR, legal, and leadership, not just the cybersecurity team. - Automate Monitoring and Reporting
Use AI-driven tools to track controls, risks, and real-time compliance status. - Test Your Incident Response Plan
Simulate cyberattacks regularly and refine your IRP based on outcomes. - Strengthen Third-Party Risk Management
Ensure vendors follow SAMA-aligned security policies and monitor them continuously. - Stay Informed on Local Updates
Subscribe to updates from SAMA, SDAIA, and the NCA to stay compliant with evolving laws. - Train Your Workforce
Conduct regular security awareness and role-based compliance training.

For tailored support, explore Wattlecorp’s SAMA Compliance Consulting Services to ensure your organisation is fully aligned with Saudi regulations.
Implementing SAMA regulations helps you stay aligned with Saudi Arabia’s evolving compliance landscape and secure your financial sector against any cyber attack. However, achieving SAMA compliance is very challenging. Avoiding common pitfalls means embracing continuous improvement, engaging with experts, and staying informed about local data privacy developments.
For the best SAMA Compliance Consulting services in Saudi Arabia, approach Wattlecorp.
With years of expertise in cybersecurity, our professional team helps you:
- Conduct gap analysis against the SAMA Cybersecurity Framework
- Implement corrective actions and controls
- Prepare for SAMA audits and reporting
- Integrate AI-driven compliance automation tools
Through approaches tailored for Saudi regulatory expectations, Wattlecorp can simplify SAMA compliance.
SAMA Compliance FAQs
1.What fines can companies face for non-compliance with SAMA regulations in Saudi Arabia?
Depending on the severity of the violation, the penalties imposed vary. Penalties can range from suspension, criminal charges, to financial penalties up to SAR 5,000 per day. When it comes to serious transgression, that includes unauthorized disclosures or misuse of confidential information, financial penalties can go even higher.
2.What is the biggest challenge with SAMA compliance in Saudi Arabia in 2025?
One of the most common hurdles is adhering to stringent cybersecurity mandates, especially when your team lacks cybersecurity awareness. SAMA compliance is more of a periodic task than a continuous process, making it difficult for organizations with outdated infrastructure to follow up.
3.How do Saudi regulations like the PDPL impact SAMA compliance?
Saudi Arabia’s Personal Data Protection Law (PDPL) safeguards KSA residents’ sensitive data, complements SAMA’s cybersecurity domains regarding data protection.







